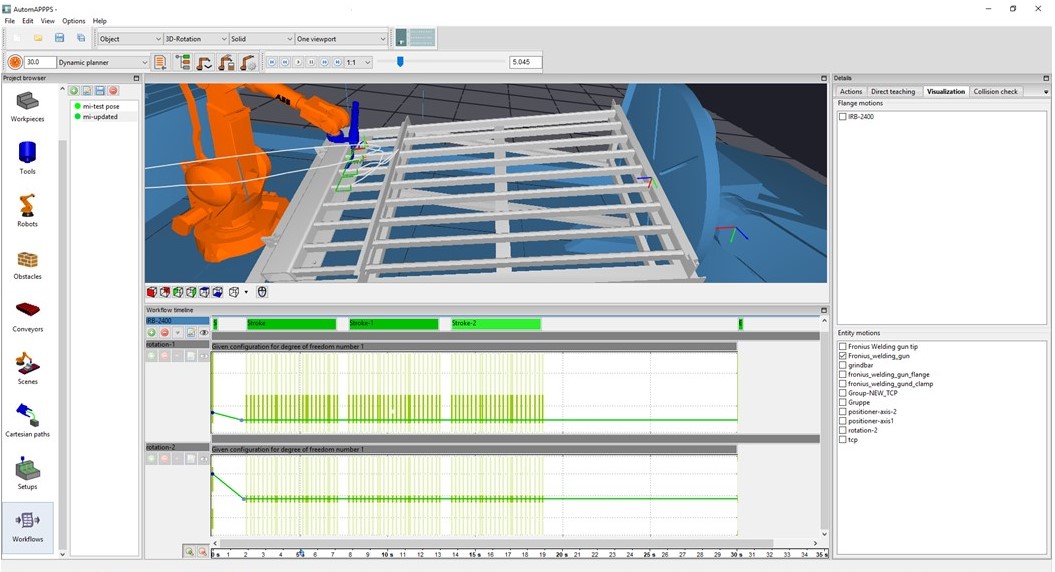
Industrial robot application programming
Industrial robot application programming
Millions of industrial robots' programs generated using AUTOMAPPPS!
AUTOMAPPPS software has proven as a solution for time and cost saving industrial robot programming. For single- and multi-robot cells with and without line-tracking. So millions of robot programs that has been generated by AUTOMAPPPS are executed each year. And when we say “millions per year”, we exclude ten million programs that were automatically planned for bin-picking or other “short jobs”.
Industrial robot programming at it's best
AUTOMAPPPS stands for industrial robot programming as it's best. Furthermore it is applicable for almost all major brands of industrial robots. Some selected robot applications and processes ideally supported by AUTOMAPPPS process models, simulation and programming are:
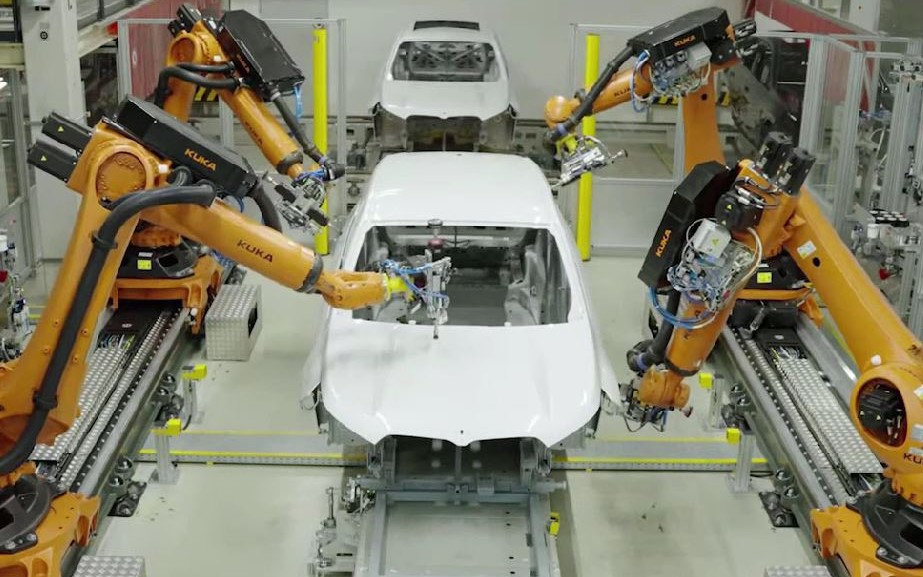
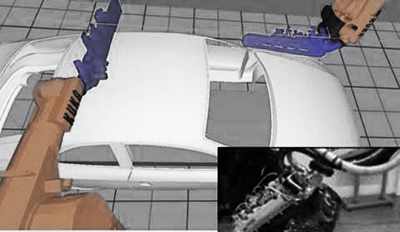
Robotic Grinding/Sanding
Example: car-body grinding:
- Optimized, validated layout
- Minimized required space and cycle time
- Minimized time and cost for robot offline programming
- Reduced test-runs, non-productive time and risks
- Cells between 1 and more than 10 robots
- Cells with and without rails, conveyors and rotatory axes
- Jobs ranging from seconds to minutes in execution time
Image courtesy of ASIS GmbH, Landshut.
Multi-Tool robotic grinding
Example: grinding for food industry:
- Fast programming for twin-headed sanding tool attached
- High surface quality for anti-bactiera properties
- Reduced test-runs, non-productive time and risks
- Compact cell with large parts and robot with rotation axis
- Jobs of very long execution time
Robotic E-coat Repair
Example: repairing detected surface defects
- Application of real time robotics
- Robots grind defects
- Input: defects detected by vision system
- 100% automated task planning
- Programming robots in seconds
- Multi-Robot system
Image courtesy of ATENSOR Engineering and Technology Systems GmbH, Austria
Robotic Belt Grinding
Example: grinding free-form parts
- Part in Hand
- Improved grinding quality
- Grinding simulation
- Reduced testing and non-productive state
- Minimized time and cost for programming and optimizing
- Reduced space required
More details after approval.
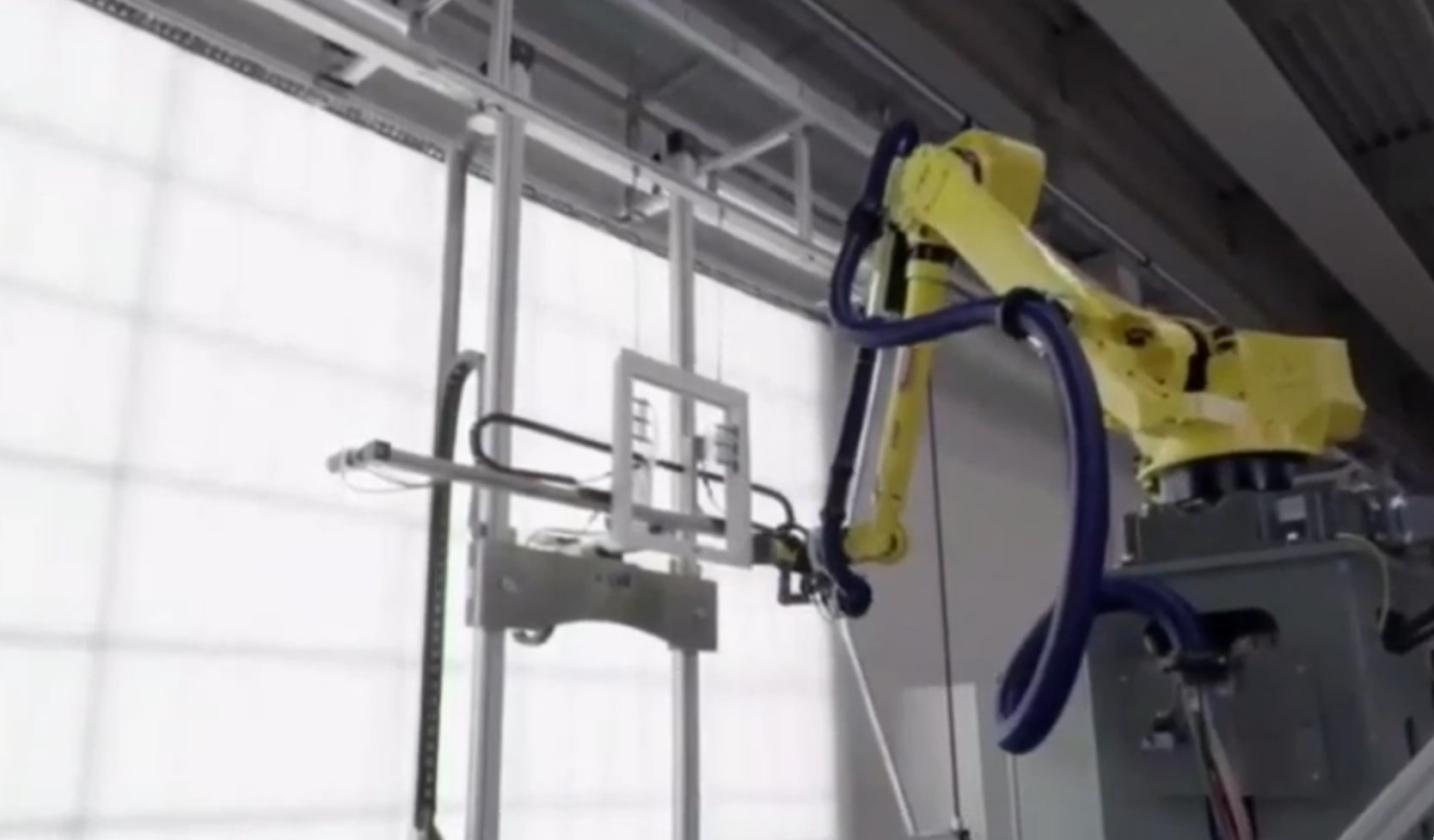
Cleaning Robots
Example: 100% cleaning of car-bodies (prior to painting)
- Improved dust removal
- WYSIWYG simulation of cleaning
- Reduced testing and non-productive state
- Minimized time and cost for programming and optimizing
- Cells with 1 to 6 robots and auxiliary axes
- Reduced space required, reduced cost for hardware
- Minimal cycle time
Image: Robot offline programming car body cleaning and validation tests together with WANDRES and a large German car manufacturer
3D Measurement - Visual CMM – Visual Metrology
Example: 3D measurement of work-pieces
- No robot experts required
- Minimized time and cost for programming
- Reduced trials and non-productive state
- Single-robot measuring cells and multi-robot systems
- Robots with and without auxiliary axes
- Minimized execution time
Image courtesy of AICON 3D Systems GmbH
Inspection
Example: 100% paint inspection
- Improving coverage and result of automation
- Optimized cycle time
- Automatic multi-robot collision avoidance - active
- Minimized time and cost for robot offline programming
- Single-robot measuring cells and multi-robot systems
- Allows for intuitive immersion into the process
Image courtesy of Micro-Epsillon Messtechnik GmbH &CoKG
Quality Control
Example: robotic control of product features
- Simple operation and robot instruction
- Automatic compensation of very large pose deviations
- Very fast instruction of the robot
- Collision free robot motions in narrow environment - automatically
- Improved OEE (overall equipment efficiency...)
Image courtesy of: confidential.
Powder Coating
Example: Robotic Powder Coating OLP
- Powder-coating and painting
- Simple and fast robot offline programming
- Simulation for reduced test-runs and optimization
- Support for line tracking
- Usually 1-2 robots
- Support for external axes
Image courtesy of Jungheinrich Moosburg AG & Co. KG, Germany
Painting
Example: Robotic Painting Offline Programming
- Simple and fast robot programming
- Up to 10,000 variants and more
- Simulation for reduced test-runs and optimization
- Support for line tracking
- Usually 1-2 robots
- Support for external axes
- Programming by shop-floor staff
Robotic Marking
Example: marking detected surface defects
- Programming robots in seconds
- Robots react on defects
- Real-time properties
- Several million programs per year
- Higher product quality
- 100,000€ savings of HW costs by software
- Savings of space in the production line
- Stop and go or conveyor tracking
- 2 or 4 robotsRemote or contact-based
High-Pressure Cleaning
Example: Robotic Cleaning
- Simple and fast robot programming
- Commonly large or complex parts
- Support for line tracking and rotation tables
- Usually 1-2 robots
- Support for external axes
- Programming by shop-floor staff
Bin-Picking
Example: high-speed random bin picking of metal parts
- Robust - frequently proven on shop-floor
- Reduced cycle time through optimal motions
- Reduced time to market and development cost
- Higher re-use: for virtually all robot manufacturers and sensors
- Fast setup and remote optimization
- Fast adaptation to different parts to handle
Image courtesy of bsAutomatisierung GmbH, Germany
Vision-based robotic sanding
Example: windown grinding
- Vision-based programming of robots
- Sensory adaption to new windows
- Lotsize-1
- Tool-path and motion planning
- Planning of robot and external axes
Image courtesy of ADLER-Werk Lackfabrik Johann Berghofer GmbH & Co KG, Austria
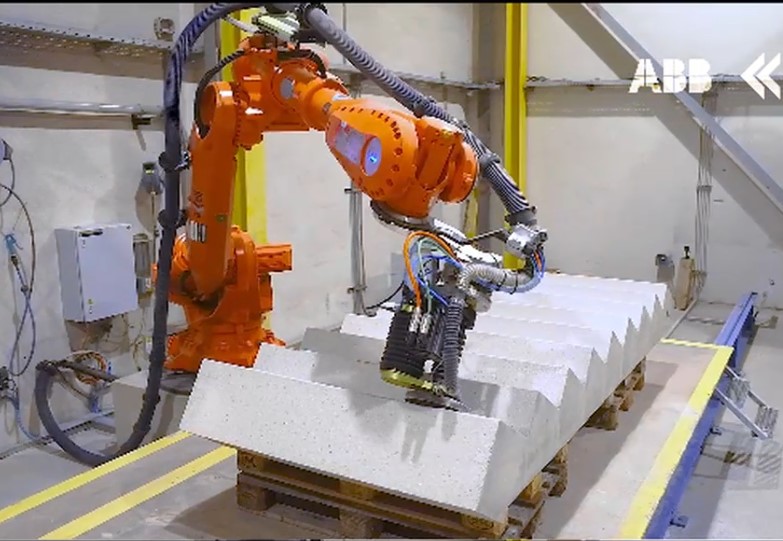
Robotic concrete grinding - with vision
Example: robots in construction industry- 3D camera based
- Fast and easy programming of grinding
- Camera-based
- Compensating shape deviations
- Compensating very large pose deviations
Vision-based deburring
Example: grinding welding seam
- Fast and easy programming of burr-following
- only grind where and as much as needed
- reducung time and tool wear
Robotic deburring
Example: robotic deburring
- Fast and easy programming of burr-following
- Motion planning in strongly structured parts
- Planning of robot and external axes
Image of robotic deburring cell courtesy of BOLL Automation GmbH, Germany
Cutting / Wood cutting
Example: robot based cutting of wood structures
- Lot size 1, automatically programmed
- CAM interface
- Robot and auxiliary axes
- Very large structures
- Collision free, precise motion in narrow environments
- Fully integrated in external GUI
More details after approval
Shape correction
Example: industrial robots cutting of shape deviation
- Lot size 1, automatically programmed
- Input from 3D vision sensors
- Corrects 3D shape of parts
- Different milling/cutting tools in hand
More details after approval
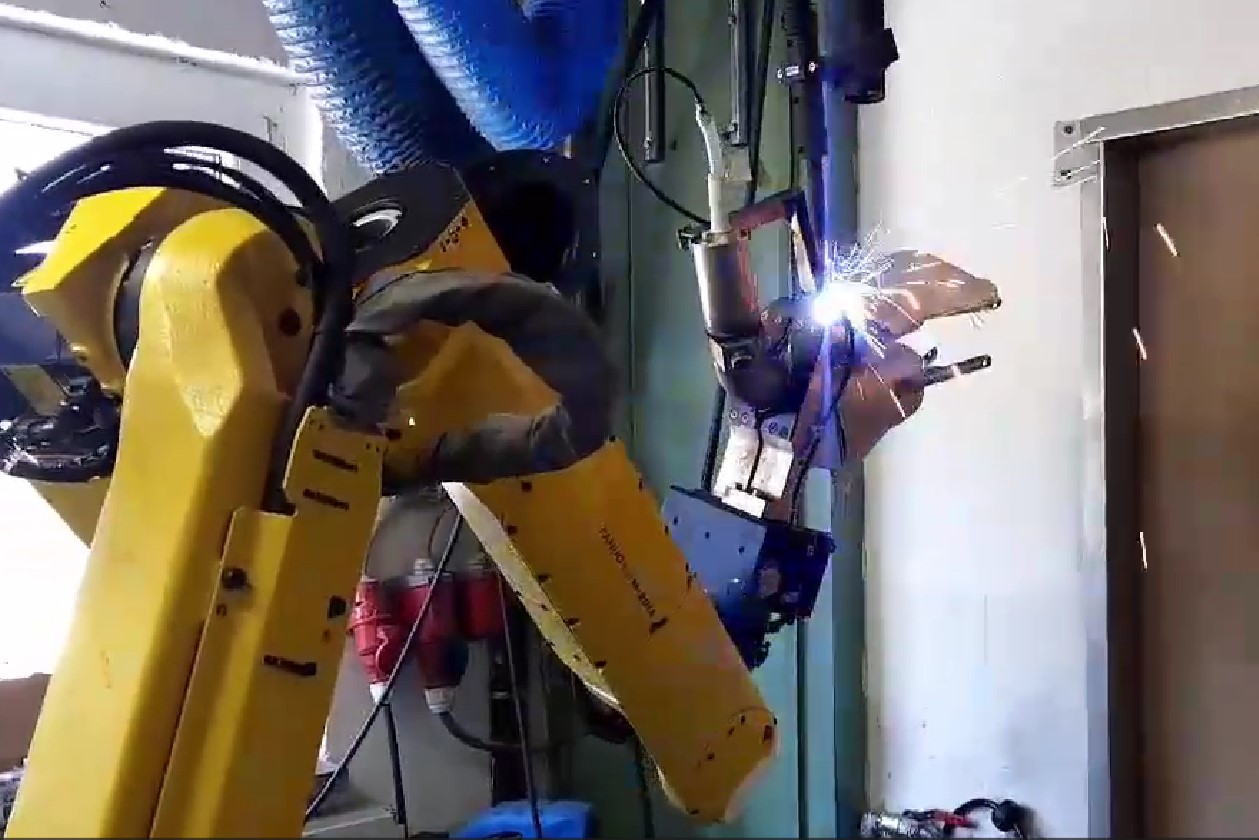
Welding
Example: Welding using 2 DOF rotation table
- Intuitive CAD-based programming
- Reduced cycle time through optimal motions
- Intutive weld-definition using CAD featurers
- Collision free motions in narrow structures
Welding
Example: Welding part-in-hand
- Intuitive CAD-based programming
- Reduced cycle time through optimal motions
- Intutive weld-definition using CAD featurers
- Collision free motions in narrow structures
Waterjet-cutting
Example: Watercutting, 2 robots
- Intuitive CAD-based programming
- Reduced cycle time through optimal motions
- Intutive weld-definition using CAD featurers
- 2 robots collision avoidance
Image courtesy of UniPro LTD
AGV + mobile manipulation
Example: industrial robots sanding boats/moulds
- Planning robot motion and AGV poses
- Very large parts and narrow corridors reach
- Special feature support for faster path definition
- Parts placed at different poses
Image courtesy of EuropeTechnologies
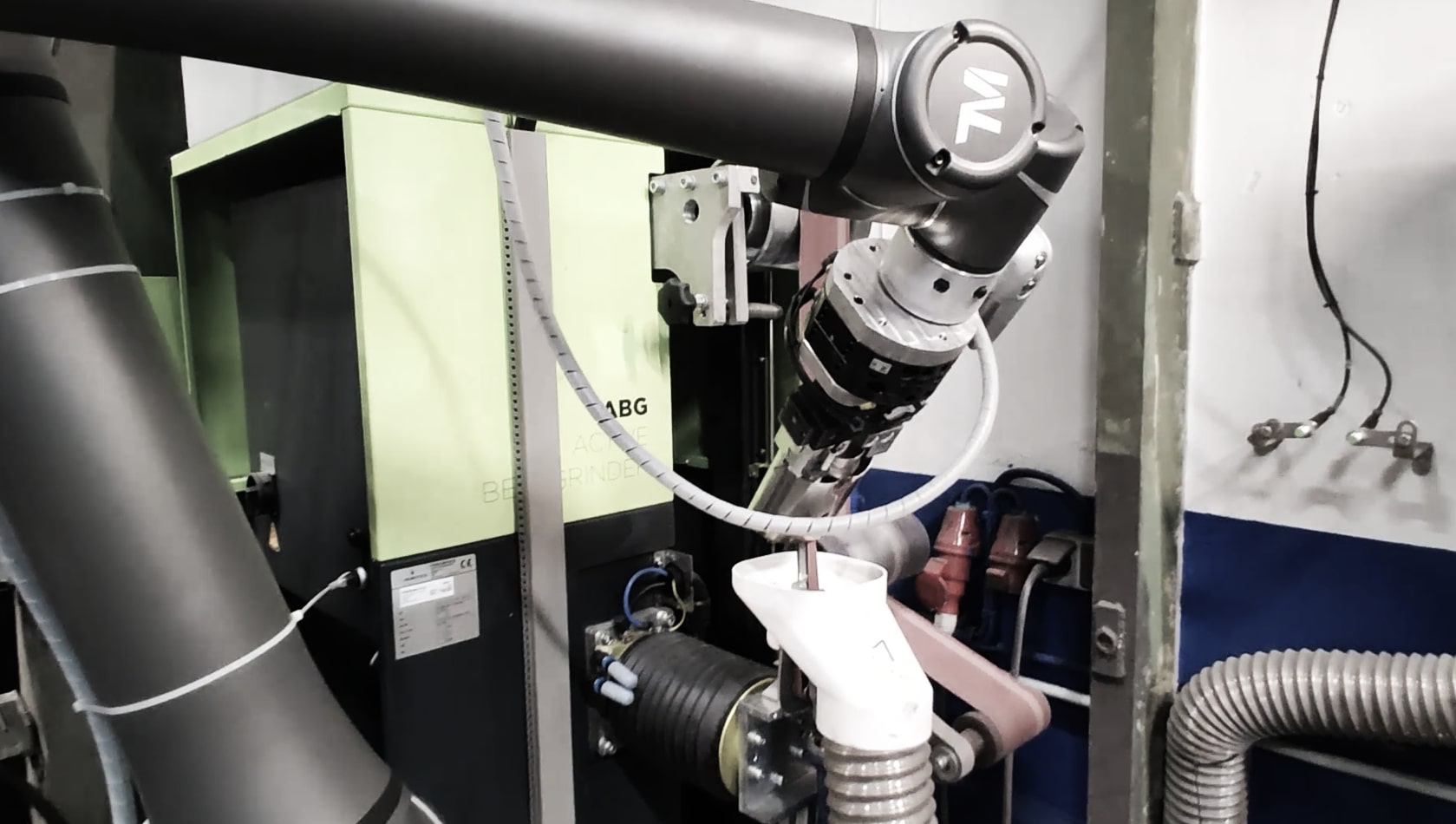
Programming Cobots
Example: programming a TechMan robot/cobot offline
- Submillimeter accuracy required
- More than 100 points
- Reflective surface
- Fast and easy programming with CAD2path replaces tedious teaching which is hard on the eyes
- Easy programming
Image courtesy of ATJ Automotive GmbH
Furthermore many more different processes have been programmed and simulated with AUTOMAPPPS robot offline programming software and fully automatic programming software. It has been successfully used with 20 different robot brands and in combination with a dozen different sensor systems.
Even narrow spaces, line-tracking in narrow cells in-between chains or skids or inside car-bodies, or multiple robots in the same working range are supported. As a result all challenges in industrial robot programming have been mastered without common iterations or extensive testing upfront.
Your process has not been listed? Send an email and find out what we can do for you.